Parts of an HVAC System: Geothermal Heat Pump
Nov 13, 2024
Author
Jake Nielson
Product Manager
Parts of an HVAC System: Geothermal Heat Pump Components Explained

When HVAC system parts break down at home it can be stressful, especially without repair knowledge.
In this blog post, I'll simplify how the components of HVAC systems work by explaining the parts of one of the most efficient and long-lasting types: a geothermal heat pump.
The goal in this is not necessarily that you'll be able to fix the issues with HVAC components on your own (though more power to you if that ends up being the case) but more to just lessen the anxiety a little by shining a light on how these systems work and give you a little more confidence in being able to confidently talk to HVAC contractors and make a good decision on how to respond when your system isn't working as expected. You can also use this article as a handy way to identify HVAC system components on your own!
1. Supply Duct

Image source
Description: Carries warm or cool air from your HVAC system into your home.
What Happens if It Fails: Damaged, dirty or leaking ducts will result in uneven temperatures, increased energy costs and poor air quality.
Routine Maintenance: Inspect for leaks, dirt, or damage and ensure ducts are sealed and insulated.
Relative Repair Cost: $$$
2. Plenum
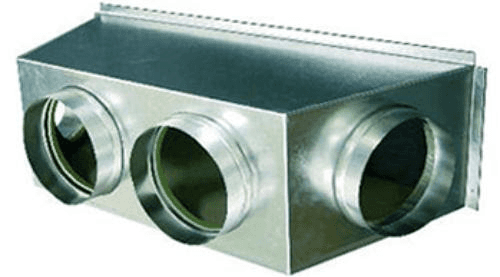
Image source
Description: An air distribution box that connects the furnace or air handler to the ductwork.
What Happens if It Fails: A cracked or leaking plenum reduces airflow, causing inefficiency.
Routine Maintenance: Regularly check for air leaks and ensure proper insulation.
Relative Repair Cost: $$
3. Condensate Drain
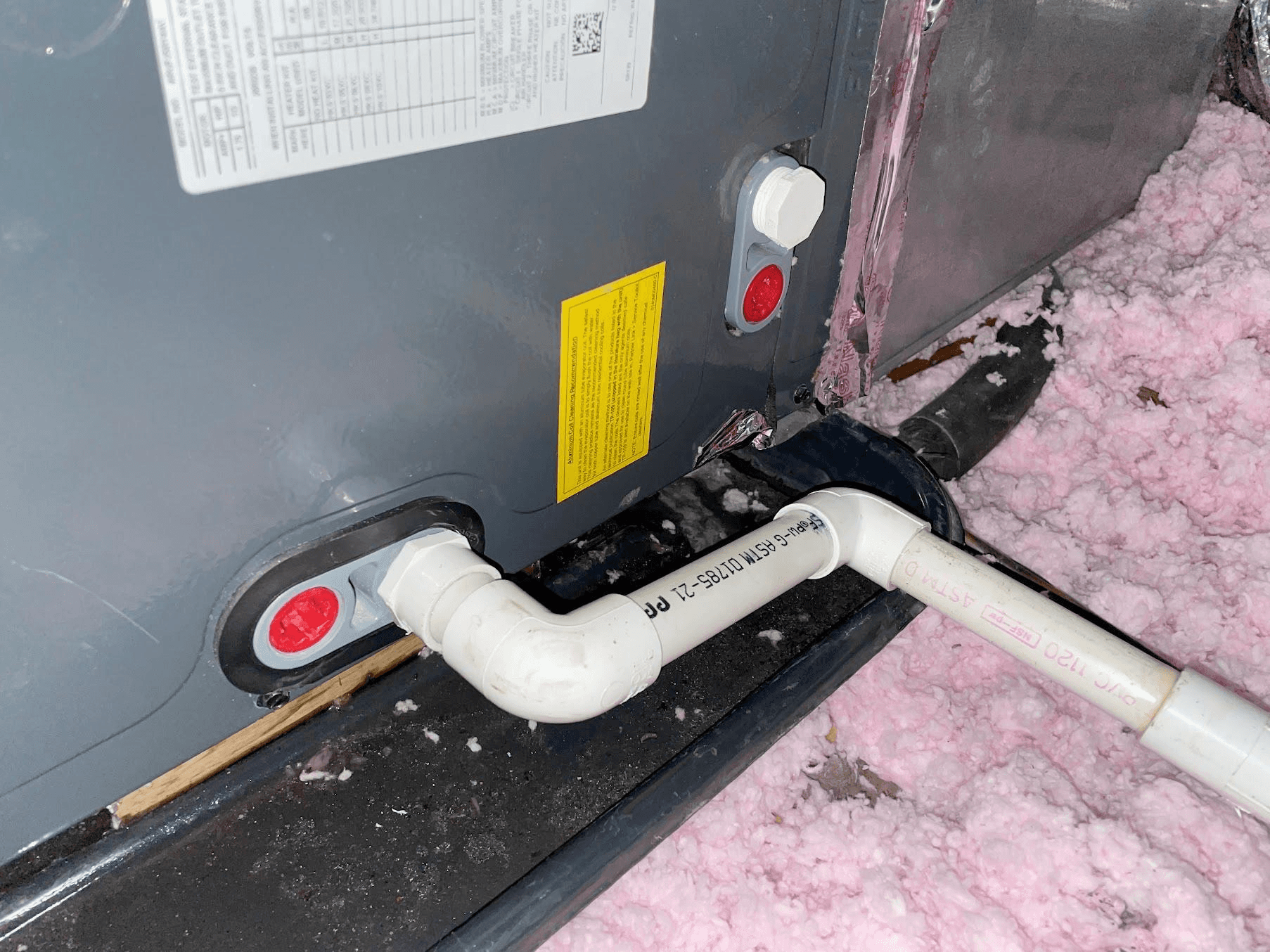
Description: Removes moisture generated during the cooling process.
What Happens if It Fails: Clogged drain can lead to water damage and mold.
Routine Maintenance: Clean the condensate drain line at least once a year to prevent blockages.
Relative Repair Cost: $
4. Return Duct

Description: Draws air from your home back into the HVAC system.
What Happens if It Fails: Reduced airflow and inconsistent temperatures.
Routine Maintenance: Inspect for any blockages or damage and ensure proper sealing.
Relative Repair Cost: $$$
5. Pressure Switch
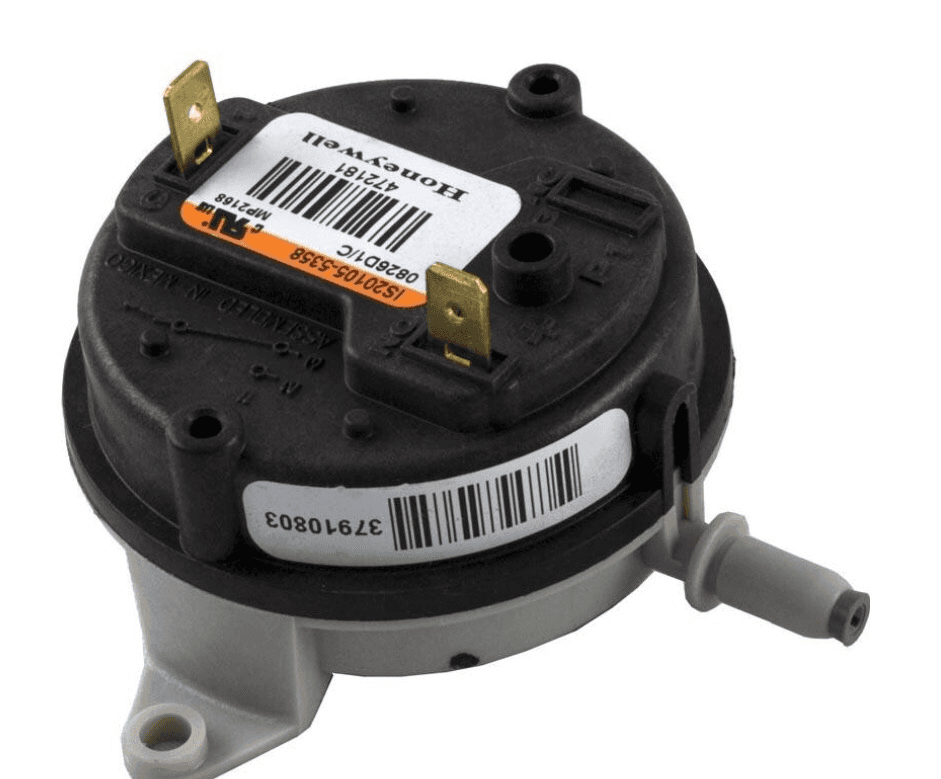
Description: A safety device that ensures proper venting of gases.
What Happens if It Fails: The furnace won’t operate to avoid unsafe conditions.
Routine Maintenance: Regularly inspect for blockages in the venting system that could affect the switch.
Relative Repair Cost: $
6. Indoor Control Board
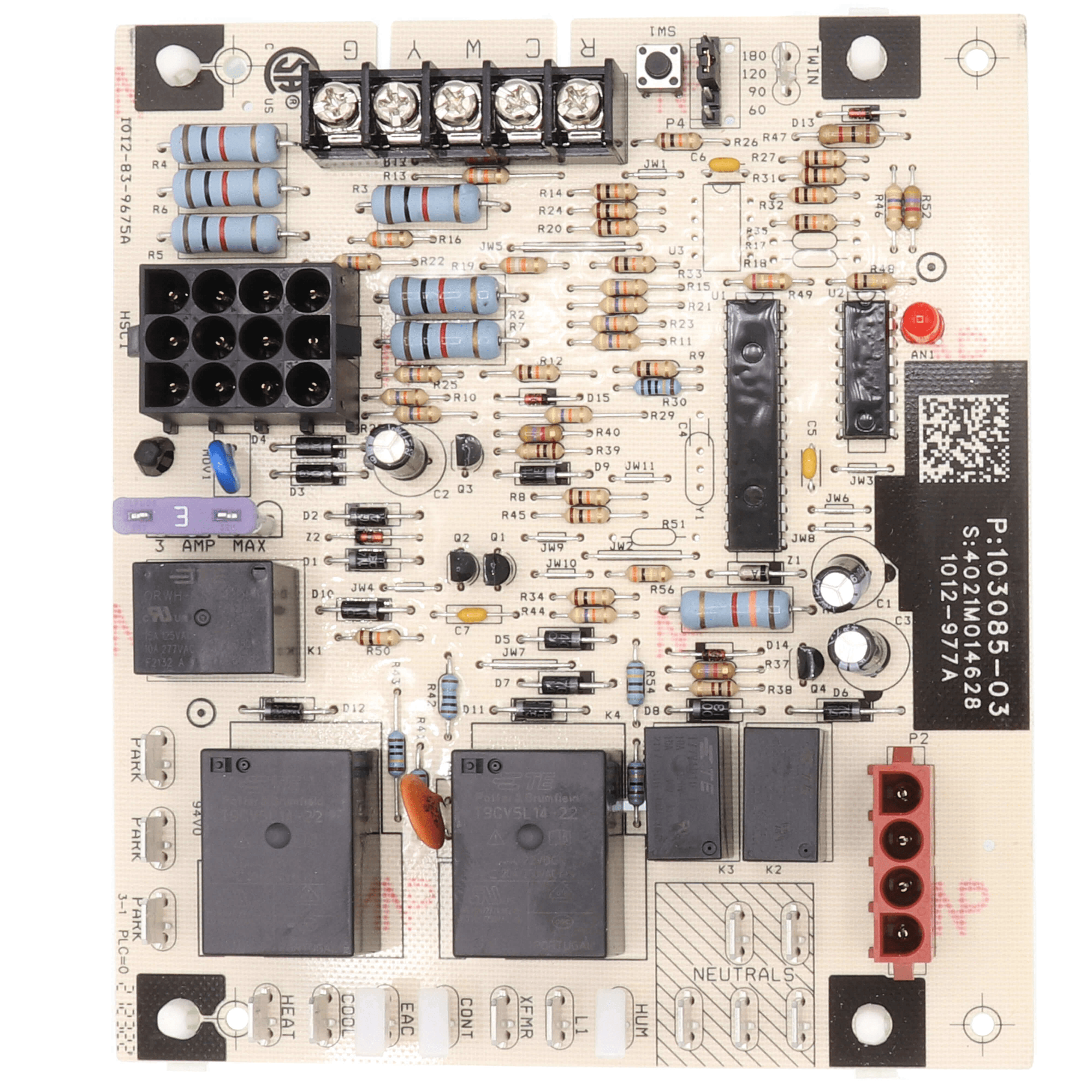
Image source
Description: Manages the operation of the HVAC system, ensuring components work in harmony.
What Happens if It Fails: The furnace or AC may not respond to thermostat settings or may malfunction.
Routine Maintenance: Have a professional inspect the control board during annual maintenance to ensure proper operation.
Relative Repair Cost: $$$$
7. Blower
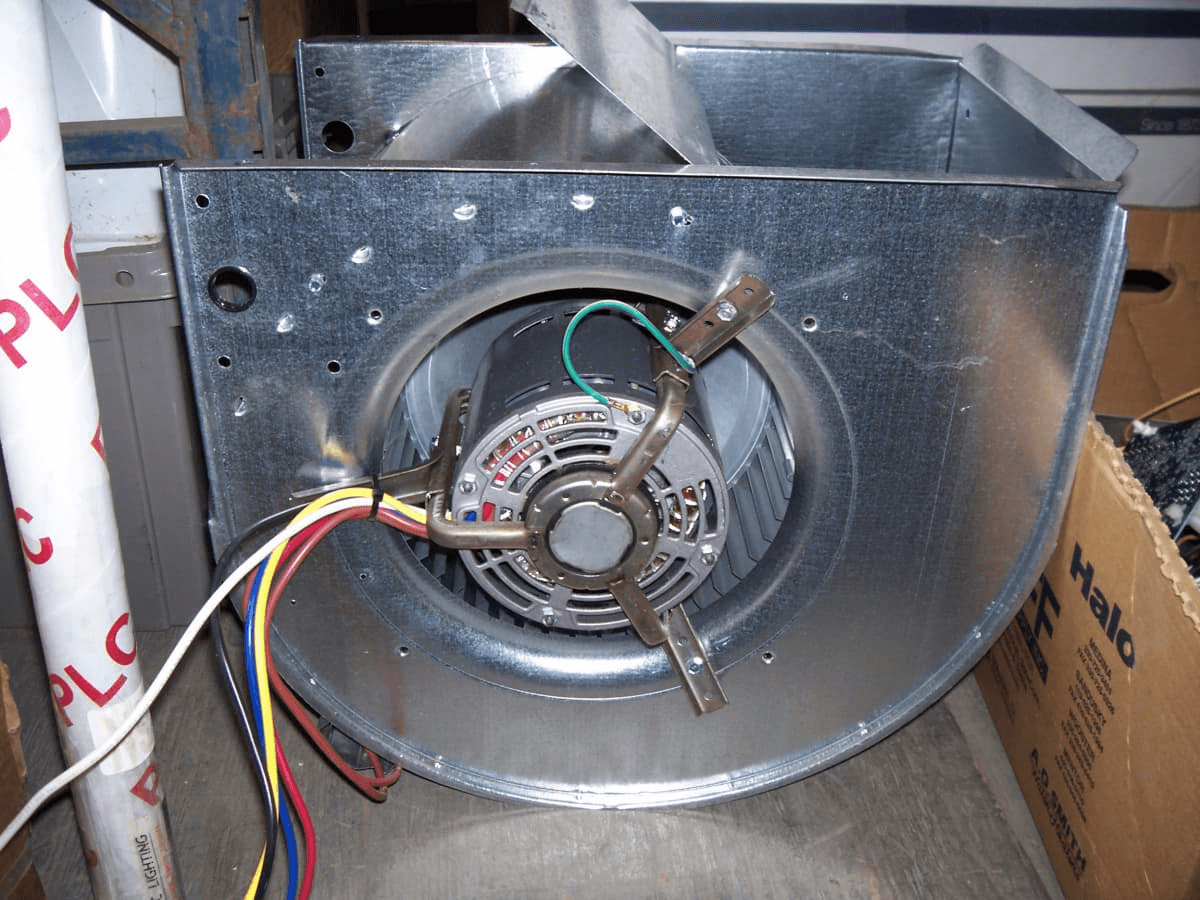
Image source
Description: Distributes heated or cooled air through the ducts into your home.
What Happens if It Fails: No airflow, meaning no heating or cooling.
Routine Maintenance: Lubricate blower components and clean out dust or debris that could obstruct airflow.
Relative Repair Cost: $$$$
8. Blower Motor
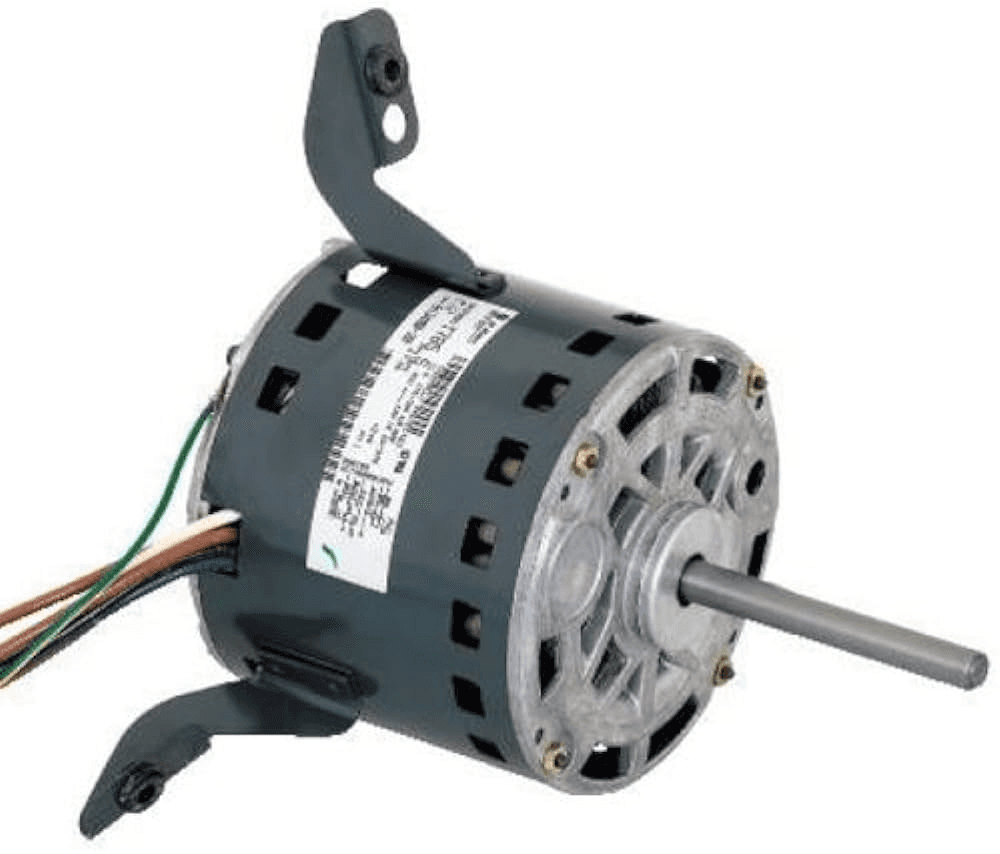
Description: Powers the blower to move air through the system.
What Happens if It Fails: The blower won’t function, preventing air circulation.
Routine Maintenance: Regularly check for signs of wear and have the motor lubricated as needed.
Relative Repair Cost: $$$
9. Blower Capacitor

Description: Helps the blower motor start and run efficiently.
What Happens if It Fails: The blower motor won’t start, leading to no air circulation.
Routine Maintenance: Check the capacitor during routine inspections to ensure it’s functioning properly.
Relative Repair Cost: $
10. Coil

Image source
Description: Absorbs or releases heat as refrigerant passes through, facilitating efficient heat exchange with the surrounding environment.
What Happens if It Fails: Can reduce heating or cooling efficiency and may cause the system to run continuously, leading to higher energy costs and potential compressor strain.
Routine Maintenance: Clean regularly to prevent dust and debris buildup. Inspect for leaks or corrosion during annual service.
Relative Repair Cost: $
11. Filter
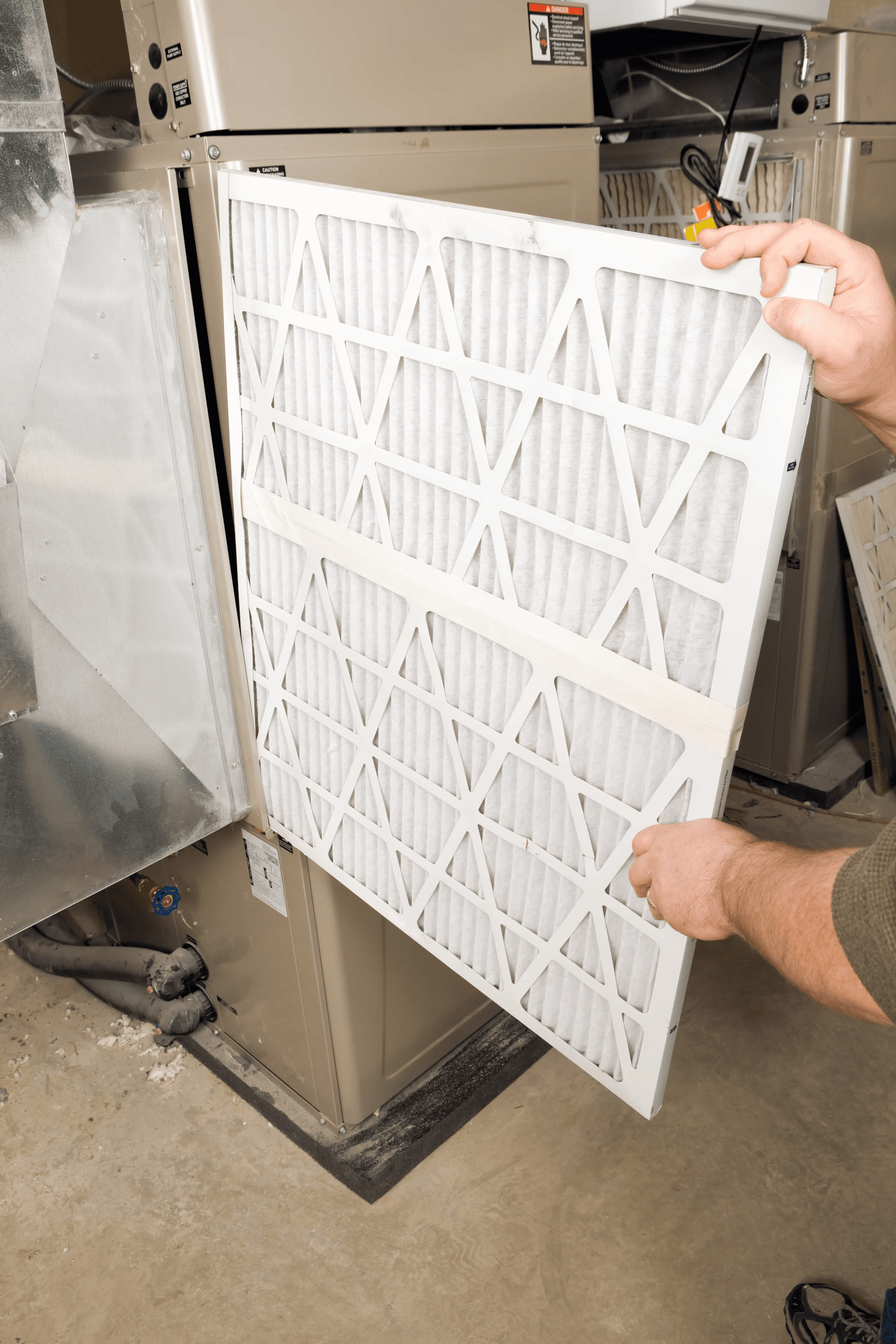
Description: Removes dust and debris from the air before it circulates through your home.
What Happens if It Fails: Reduced airflow, poor indoor air quality, and potential system strain.
Routine Maintenance: Replace the filter every 1-3 months, depending on usage and filter type.
Relative Repair Cost: $
12. Filter Drier

Image source
Description: Removes moisture and impurities from the refrigerant to protect the geothermal system’s components.
What Happens if It Fails: A failed filter drier can allow contaminants into the system, leading to reduced efficiency and potential damage to the compressor.
Routine Maintenance: Replace regularly to ensure effective filtration and prevent clogging.
Relative Repair Cost: $
13. Ground Loop Heat Exchanger

Image source
Description: Facilitates heat transfer between the ground loop and the refrigerant, enabling the geothermal system to provide heating and cooling.
What Happens if It Fails: A damaged heat exchanger can reduce efficiency or cause the system to overheat, potentially leading to breakdowns.
Routine Maintenance: Regularly inspect for wear, corrosion, and leaks.
Relative Repair Cost: $$$$
14. Ground Loop Pump
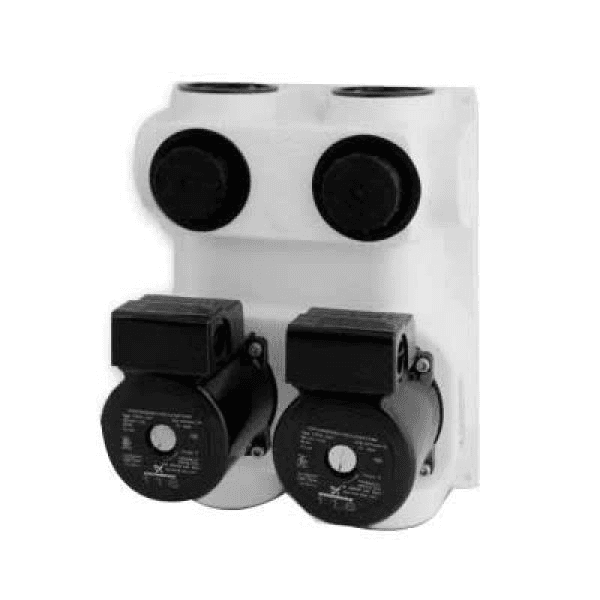
Image source
Description: Circulates water or a water-antifreeze mixture through the underground ground loop, allowing heat transfer between the earth and the geothermal heat pump.
What Happens if It Fails: Water circulation stops, preventing heat exchange with the ground and causing the system to lose its heating and cooling capability.
Routine Maintenance: Check for proper operation, inspect for leaks, and ensure the pump is free of debris; replace any worn parts as needed.
Relative Repair Cost: $$$
15. Ground Loop

Image source
Description: A series of underground pipes that circulates water or refrigerant, transferring heat between the earth and the geothermal heat pump.
What Happens if It Fails: Leaks or blockages in the ground loop can prevent heat transfer, significantly reducing system efficiency or stopping it altogether.
Routine Maintenance: Inspect for leaks and pressure issues; annual pressure testing may be required.
Relative Repair Cost: $$$$$
16. Transformer
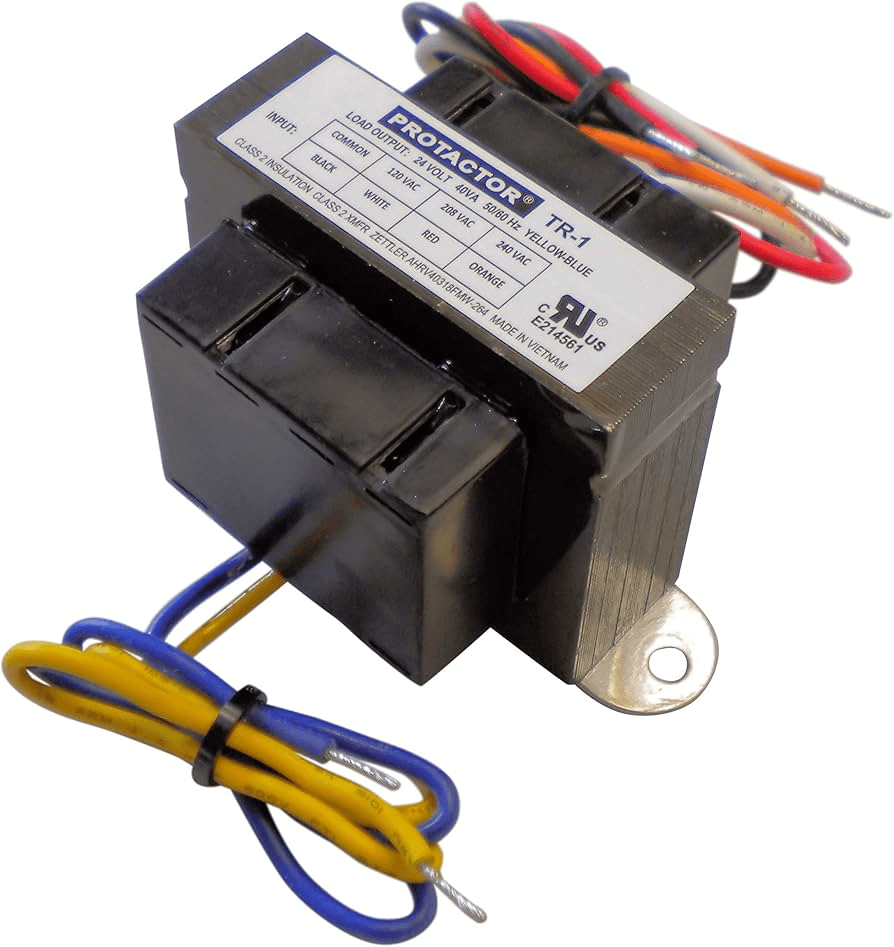
Image source
Description: Steps down high voltage for furnace and air conditioning components.
What Happens if It Fails: The HVAC system won’t operate due to insufficient voltage.
Routine Maintenance: Have a professional inspect the transformer during annual maintenance.
Relative Repair Cost: $$
17. Compressor
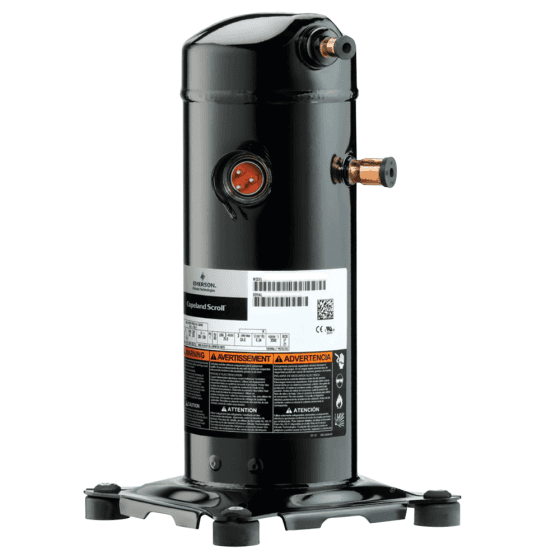

Image source
Description: Circulates refrigerant between the evaporator and condenser coils.
What Happens if It Fails: The AC won’t cool the air, and the entire system may need to be replaced.
Routine Maintenance: Check refrigerant levels and clean debris from around the outdoor unit to prevent overloading the compressor.
Relative Repair Cost: $$$$$
18. Pressure Switch (AC)
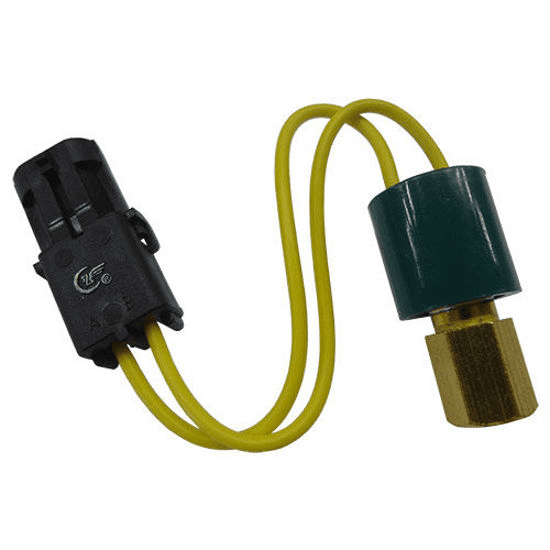
Description: Ensures safe refrigerant pressure levels during AC operation.
What Happens if It Fails: The system may shut down to prevent damage from incorrect refrigerant levels.
Routine Maintenance: Check refrigerant levels during maintenance to ensure the pressure switch works properly.
Relative Repair Cost: $
19. Capacitor
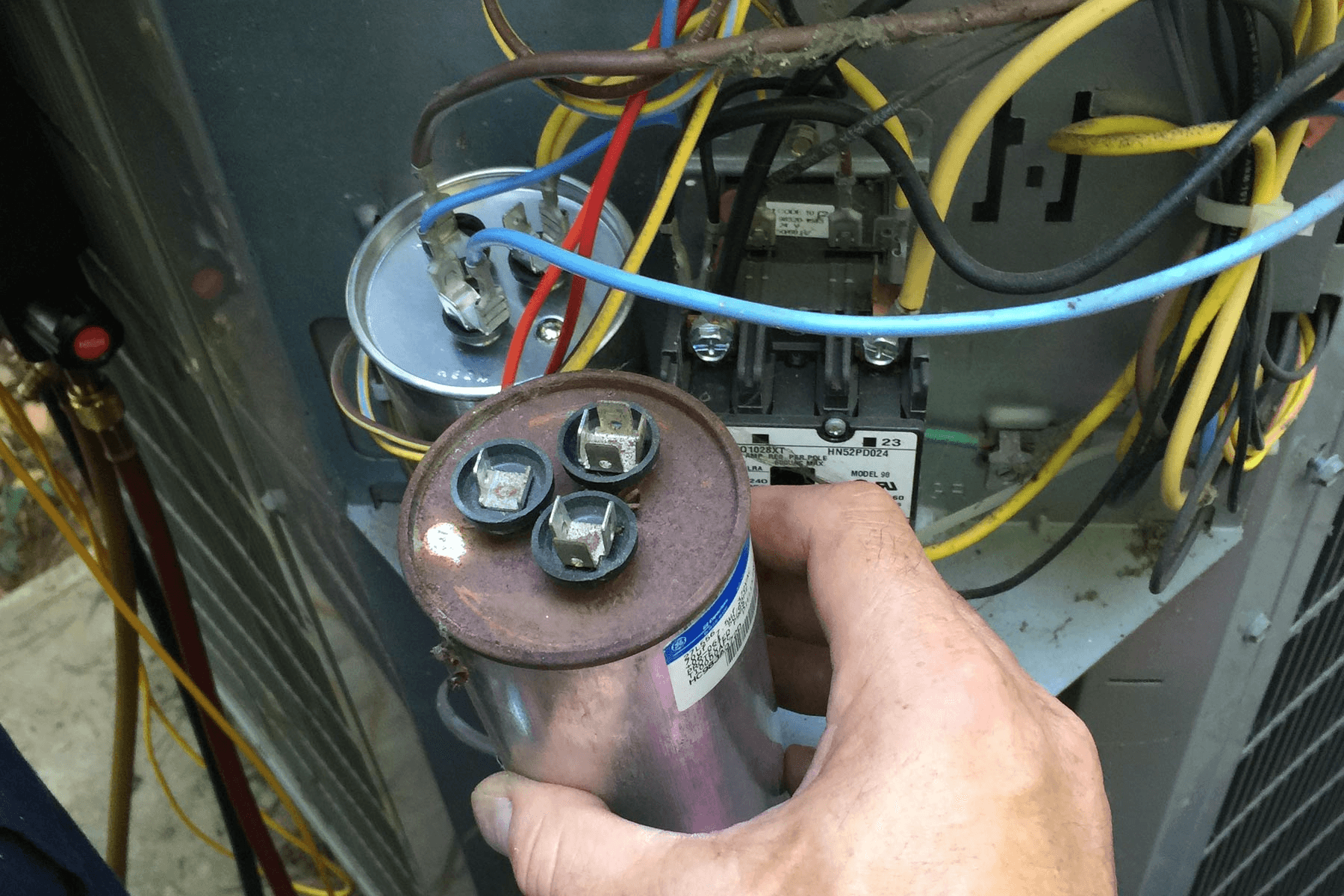
Image source
Description: Stores and releases electrical energy to help start and run the compressor and fan motors efficiently.
What Happens if It Fails: The system’s motors may struggle to start or won’t run at all, leading to reduced performance or complete system shutdown.
Routine Maintenance: Check for signs of wear, bulging, or leakage during regular maintenance, and replace if necessary to prevent unexpected failures.
Relative Repair Cost: $
20. Desuper Heater Coil
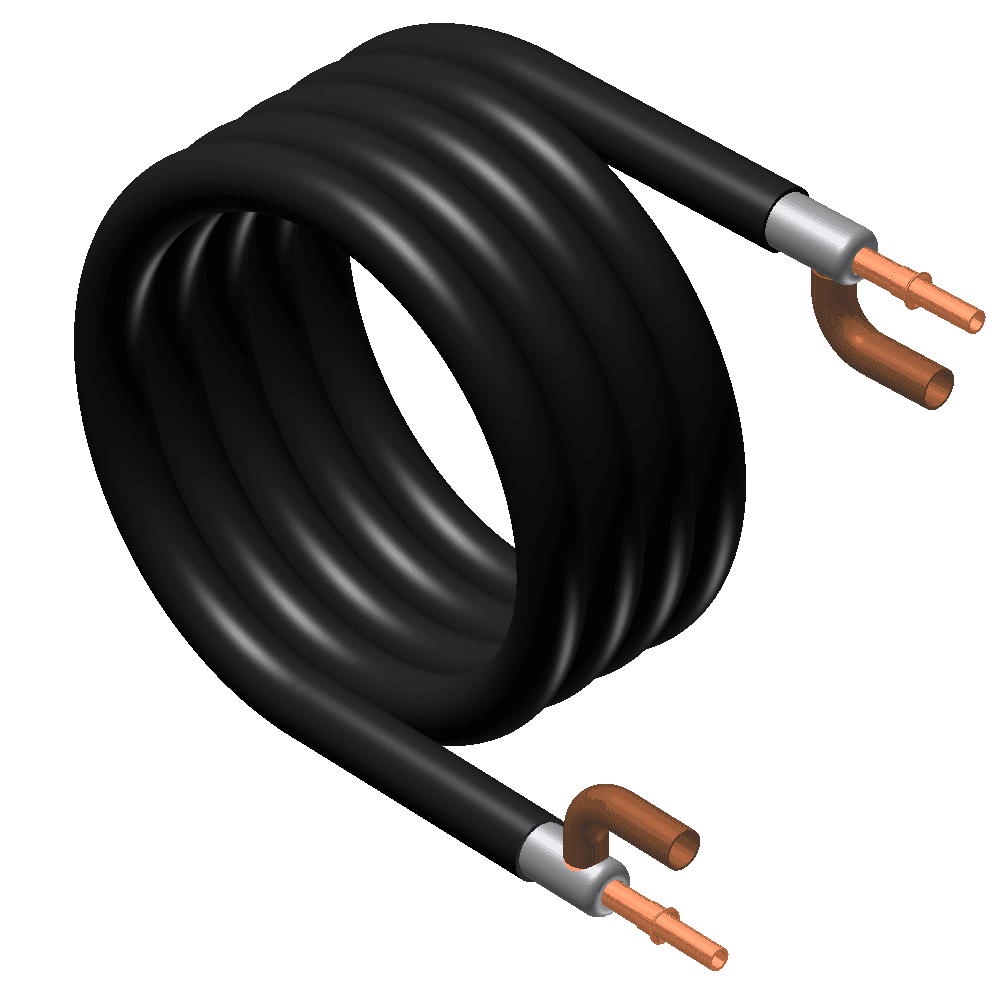

Image source
Description: A heat exchanger that captures excess heat from the geothermal system to preheat water for a water heater, improving efficiency.
What Happens if It Fails: It won’t transfer heat effectively to the water heater, reducing overall efficiency and increasing energy costs.
Routine Maintenance: Inspect for corrosion and mineral buildup; clean the coil as needed to ensure effective heat transfer.
Relative Repair Cost: $$$
21. Desuper Heater Pump
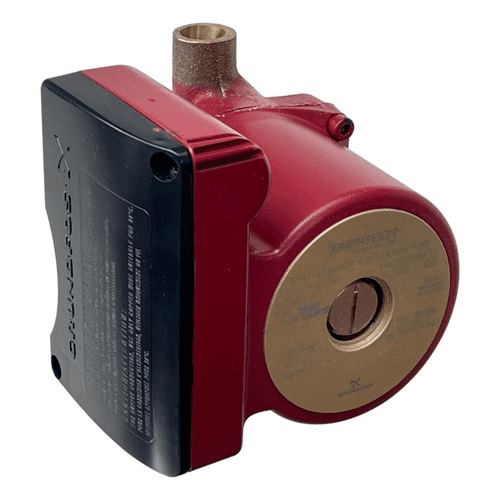

Image source
Description: Transfers excess heat from the geothermal system to assist in heating water.
What Happens if It Fails: There is no additional heat for water, causing the water heater to work harder and increasing energy costs.
Routine Maintenance: Check for proper operation and any leaks during annual service.
Relative Repair Cost: $$
22. Water Heater
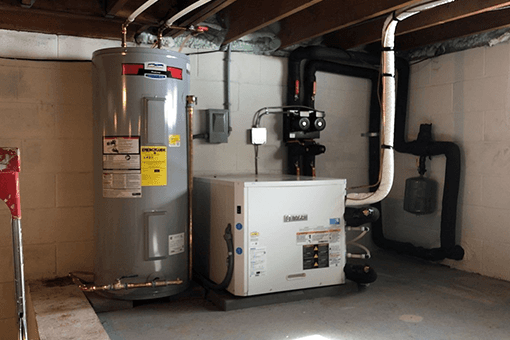
Image source:
Description: Stores and heats water, and when connected to the desuperheater, it utilizes heat from the geothermal system to improve efficiency.
What Happens if It Fails: There is no hot water.
Routine Maintenance: Flush the tank annually and check for leaks or corrosion.
Relative Repair Cost: $$$
23. Water Heater Supply
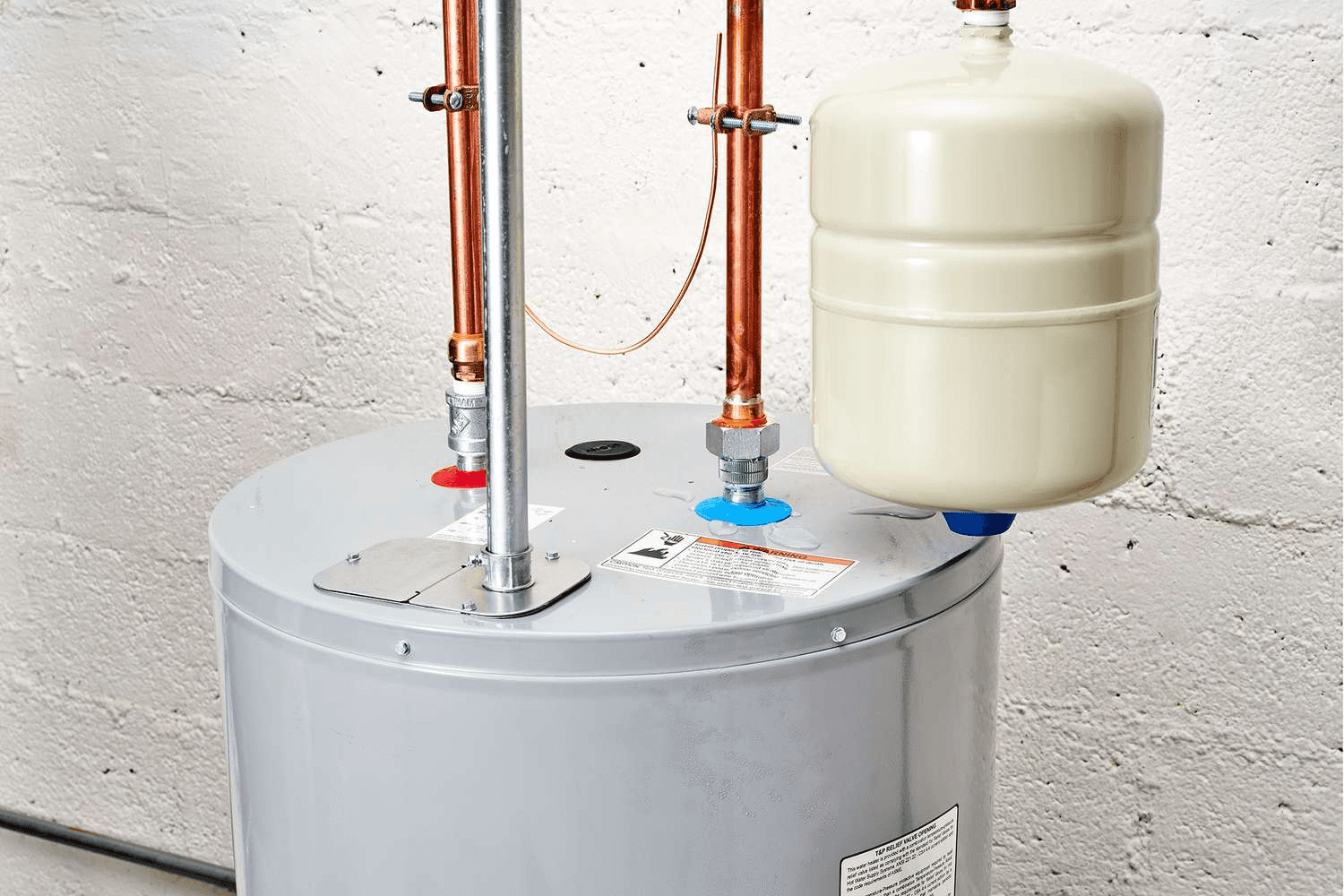
Image source
Description: The cold water supply brings unheated water into the water heater for heating. The hot water supply line distributes heated water from the water heater to taps and appliances.
What Happens if It Fails: A leak or blockage in the cold water supply can reduce water flow, preventing sufficient heating. A failure in the hot water supply can lead to reduced water pressure or no hot water reaching fixtures.
Routine Maintenance: Check for leaks, especially around joints and fittings.
Relative Repair Cost: $$
24. Thermostat
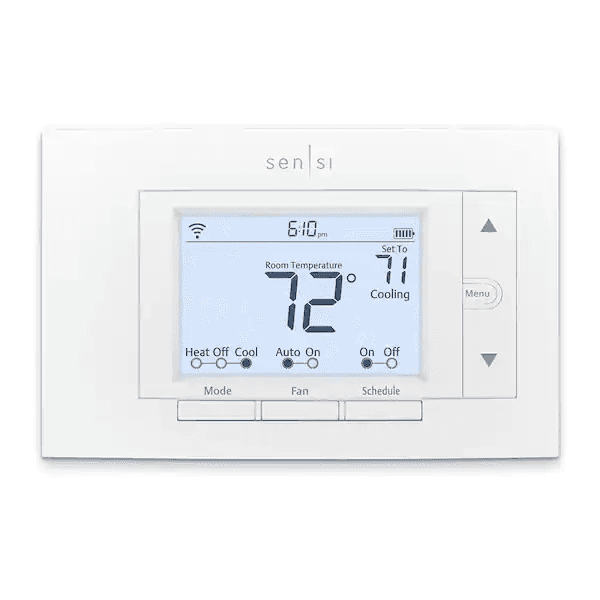
Description: Controls the temperature in your home by communicating with the HVAC system.
What Happens if It Fails: The HVAC system won’t respond to temperature adjustments, leading to discomfort.
Routine Maintenance: Test the thermostat for accuracy and recalibrate if necessary during annual system checks.
Relative Repair Cost: $$
Conclusion
By understanding HVAC unit components and performing routine maintenance, you can extend the life of your equipment and avoid costly repairs. From cleaning coils and filters to inspecting the control board and compressor, each component requires specific care to ensure it functions properly. Schraer Air Experts are here to help with all your HVAC maintenance needs, ensuring your system runs efficiently year-round.


